Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs) are chips responsible for transforming, distributing, detecting, and managing electrical energy within electronic device systems. They primarily identify the power supply voltage for the CPU, generate corresponding short-junction waves, and drive the power output of subsequent circuits. This article provides a detailed introduction to the classification and various features of the power management chips from Xinbole XBLW - Analog Chips, hoping to provide a deeper understanding after reading.
01—Description
Chips, also known as semiconductor devices, are crucial components in electronic devices, and there are various types of chips. They can be classified into analog chips and digital chips based on the operation mode of transistors.
Analog circuits are primarily composed of capacitors, resistors, transistors, and other components. Analog integrated circuits integrate these analog circuits together to process continuous function-form analog signals (such as sound, light, temperature), serving as a type of integrated circuit. The source of all data is analog signals, and analog chips serve as the first gateway for processing external data.
Analog chips come in a wide variety and have broad application scopes. Apart from common analog chips such as signal chains and power management, specialized products like RF devices in the communication field and memory interface chips in the server domain also fall under the category of analog chips. Below is an illustration of an analog chip.
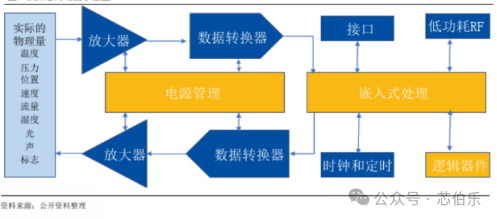
From the perspective of transmitting weak electrical signals and managing strong electrical energy, analog chips are divided into signal chain chips and power management chips. Power management chips can be further categorized into AC/DC (alternating current to direct current) converters, DC/DC (direct current to direct current) converters, driver ICs, protection chips, LDOs (low-dropout regulators), load switches, PMICs (power management integrated circuits), etc.
02—Power Management Chips
Regarding power management chips from Xinbole XBLW, the mainstream DC/DC chips include buck (step-down), boost (step-up), buck-boost converters, as well as PWM (pulse-width modulation) control ICs used to drive external switches.
1. Buck-boost converter chip: XBLW MC34063

XBLW MC34063
Characteristics:
- Wide operating voltage range from 3V to 40V
- Extremely low static power consumption
- Limited current function with a maximum output current of 1.5A
- Adjustable output voltage, operating frequency up to 100kHz
- Output voltage accuracy of 2%
LM317 Positive Voltage Regulator and LM337 Negative Voltage Regulator, as well as the three-terminal regulators L78 and L78M series.
LM317 Main Performance Parameters:
Input voltage: 3-40V
Output voltage: Adjustable from 1.25-37V
Three current output versions: 0.1A, 0.5A, and 1.5A
The chip internally incorporates overheat, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection circuits.

LM337 is a three-terminal adjustable negative voltage regulator with an output current of 1.5A. It has an input voltage range from -3V to -40V and an output voltage range from -1.2V to -37V. It features built-in thermal overload protection, short-circuit protection, overcurrent limitation, and overheat protection.
The L78M series chips are available in various output voltage versions, including 5/6/8/9/12/15/18/24V. They have an output current of 0.7A, a minimum dropout voltage of 2V, a minimum input voltage of 7V, and a maximum input voltage of 38V. These chips also feature built-in thermal overload and short-circuit protection, making them excellent performers as DC-DC step-down regulators.

③ AMS1117 Series Low Dropout Linear Regulators
The AMS1117 series of low dropout linear regulators have an output current capability of up to 1A. While some other brands may claim an output current of 800mA, with some even marking 1A, the actual performance often falls short.
However, Xinbole XBLW's AMS1117 doesn't exaggerate its capabilities. After leaving the factory, it undergoes multiple load tests, power ripple tests, and load transient response tests. Its performance is stable, and its quality is superior.
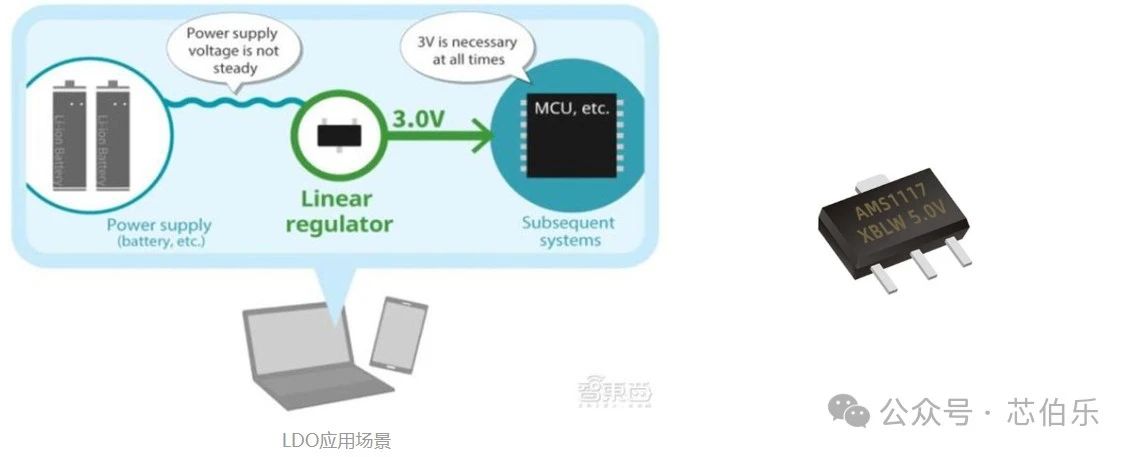
03—Main Features
- Only requires two external resistors; the ADJ version allows adjustable output voltage ranging from 1.25V to 13.8V.
- Available in various fixed voltage output versions: 1.2V, 1.5V, 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.85V, 3.3V, and 5V.
- Output current of 1A, output voltage accuracy of ±1.5%, operating voltage up to 15V.
- Voltage linearity less than 0.2%, load regulation rate less than 1.0%.
④ PWM Pulse Width Modulation Control Chip
Xinbole XBLW UC38 series is a PWM control chip with an internally fixed frequency current mode. It operates at frequencies up to 500kHz and comes in 8-pin small DIP and SOP packages. This series of chips has high integration and can achieve high-performance control of switching power supplies. Its advantages include low power supply current (startup current of 0.05mA, static current of 5mA), built-in frequency compensation network, built-in soft-start function, built-in over-temperature protection, etc. The UC38 series chips have multiple startup voltage versions and duty cycle versions and are used in applications such as switch-mode power supplies, power regulation, and current mode flyback circuits.

04—Product Applications
From smartphones, tablets to wearable devices, from household appliances to electric vehicles and drones, almost all modern electronic devices rely on power management chips to ensure their performance and safety. Power management chips can enhance the stability and reliability of devices, extend battery life, improve energy utilization efficiency, and provide functions such as overload protection and overheat protection, ensuring that devices can operate safely and stably. With the development of technology, power management chips are also constantly evolving to meet increasingly complex and efficient power management requirements.
05—Conclusion
As electronic devices continue to evolve towards smaller size and higher performance, power management chips also face many challenges. Xinbole (XBLW)'s future development trend will focus on improving integration, optimizing energy efficiency, enhancing compatibility and versatility, and exploring the application of new materials and technologies.
Recommend News
-
Phone
400-9682 003